5 Things to Consider Before Getting a New Motherboard
The motherboard is the most critical part of any personal computer. It serves as the backbone into which nearly all other parts and components inside your machine must be connected to function — processor, memory, graphics card, storage, and more.
Your choice of motherboard impacts many other factors, such as the CPU it can support, the type and quantity of RAM sticks you can insert, and the number of expansion slots and connectivity ports. Learn how to choose a motherboard by considering these five critical factors.
1.CPU Compatibility
Each motherboard has a socket to support a particular range of CPUs. For example, the latest high-end motherboards may feature an AM5 socket to support AMD Ryzen processors or an LGA 1700 socket for the latest Intel i-series CPUs. If you have a specific CPU in mind, select a motherboard with the correct socket.
Below is a list of currently available CPU sockets and a few examples of compatible desktop CPUs:
| Socket Type | Compatible CPU Families |
| AMD AM4 Socket |
|
| AMD AM5 Socket |
|
| Intel LGA 1700 Socket |
|
2. Motherboard Chipset
Each motherboard also comes with a Platform Controller Hub (PCH), commonly referred to as a chipset, to manage the transfer of data between the CPU and its components. Higher-end chipsets support more connectivity ports and faster data transfer rates, allowing you to fully utilize your graphics cards, high-speed storage, or latest-generation USB ports.
For example, a motherboard with an AM5 socket may feature one of four different chipsets — from the entry-level B650 to the mid-range B650E and X670 and the high-end X670E.

3. Form Factor
Desktop computer motherboards are available in various form factors to match computer cases of different sizes. Choose a motherboard that fits well with a case that’s the right size. Here are some common motherboard form factors and the types of PC builds they’re typically used for:
- ATX: The standard motherboard form factor that has been in use since 1995. ATX is sometimes called “full-size” because ATX boards are primarily intended to fit inside standard-sized desktop PC cases.
- microATX: This form factor is approximately 20 percent smaller than standard ATX, making it suitable for more compact PC builds. However, microATX boards typically have fewer ports and connectivity than full-size equivalents.
- Mini-ITX: This is the smallest mainstream form factor for home PCs. Mini-ITX boards are over 60 percent smaller than ATX equivalents, making them ideal for building mini-PCs. They sacrifice connectivity and parts flexibility to maximize portability.
- eATX: Also known as Extended ATX, this form factor is up to 35 percent larger than ATX. eATX boards are mainly intended to build high-powered machines suitable for high-end gaming, content creation, 3D rendering, or home server applications.
4. RAM Compatibility and Capacity
Random Access Memory (RAM) sticks give your machine the power to handle more programs, improve gaming performance, and generally make it feel more responsive. Motherboards determine your PC’s RAM compatibility in the following ways:
- RAM generation: Modern motherboards typically support DDR5 RAM sticks, which are faster and more performant than previous-generation DDR4 models. This is the most important compatibility element to check. Motherboards designed to accept a specific DDR generation are physically incompatible with RAM sticks of other generations.
- RAM slots: Each motherboard may only accept a limited number of RAM sticks, typically 2 to 4, depending on its form factor.
- RAM speed: RAM sticks come in different speed ratings, measured in megahertz (MHz). The faster the RAM, the more efficiently it can handle and transfer data. Check the motherboard specifications sheet to determine the maximum RAM speed it can handle. Inserting RAM sticks with a higher speed rating than the motherboard can handle may still work but be throttled to the board’s maximum rate.
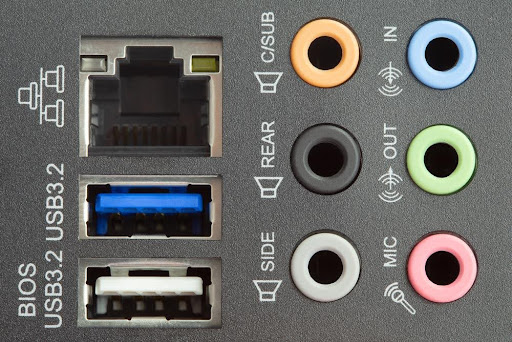
5. Expansion Slots and Connectivity
Motherboards come with a wide range of expansion slots and connectivity ports, each capable of supporting numerous internal components and accessories. Your choice of motherboard model determines the type and number of slots and ports it features, influencing the types of components and peripherals you can connect.
Here are some of the most important slots, ports, and connectivity features to look for in a motherboard:
- PCI Express (PCIe) ports: One of the largest expansion slots available on motherboards today is PCIe slots. Most modern boards feature at least one PCIe x16 slot for graphics cards, whereas other, shorter PCIe slots (x1, x4, x8) can accommodate sound cards, network cards, and certain solid-state drive (SSD) models.
- M.2 slot: Modern motherboards feature at least one M.2 slot, which can accept the latest-generation NVMe storage drives.
- USB ports: Many motherboard models can accept USB devices through various ports. The most common are Type-A (rectangular) and USB-C, similar to the type used by mobile phones. USB Type-A ports with a blue port are USB 3.0 or later and feature the fastest transfer speeds.
- SATA ports: Although M.2 slots and NVMe drives are the current standard for data storage, most motherboards feature SATA ports for connecting additional drives. SATA ports require dedicated SATA cables, which you can use to connect previous-generation SSDs.
- Wireless connectivity: Check the motherboard specifications sheet for compatibility with wireless devices like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. Built-in wireless connectivity lets you connect multiple devices to your machine — from Bluetooth audio devices to connecting to the internet via Wi-Fi.
- Ethernet port: If you prefer to use a wired internet connection or need it, check for an Ethernet port. High-end models are compatible with the latest Ethernet cable generations, which can support speeds of up to 10 Gbps, ideal for taking full advantage of fiber-optic internet.
Future-Proof Your PC with a Motherboard Upgrade
Upgrading your computer’s motherboard requires you to consider many parts and components. However, with care and a little preparation, the benefits are undeniable: compatibility with the latest-generation processors, GPUs, storage, RAM, and connectivity options. These allow you to bring your machine to the current hardware generation, ensuring it is ready for any task you can throw at it.
